AS-MS for Binding Interactions Evaluation
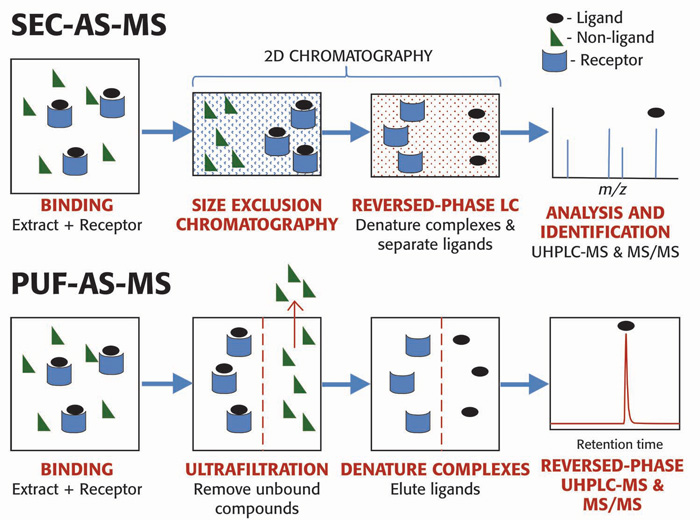
Fig.1 Two methods of AS-MS: SEC-AS-MS and PUF-AS-MS. (Richard, B.; Van, B. 2020)
As an important high-throughput screening technique, AS-MS owns unique benefits of label-free and short time to screening. It identifies small-molecule ligands of biological targets and provides their chemical structures to deliver high-quality hits for further optimization. AS-MS techniques are able to assess the binding of candidate molecules to immobilized or soluble receptors, and these methods are proven to be as valuable complements to drug discovery technologies. Moreover, as a label-free binding assay technology for the analysis of interactions between targets and small drug molecules, AS-MS does not require modification of targets or compounds.
Process of AS-MS
Target proteins and compound pools are incubated and interacted firstly. AS-MS then isolates pharmacologically active compounds from mixtures utilizing binding interactions between ligands and receptors. And they can be dissociated and identified successfuly by mass spectrometry.
AS-MS Services
- Our team provides services of rapid screening of large amount of compounds to identify ligands for a specific biomolecular target.
- We can identify the active component through the calculation of the difference mass value between the complex and the protein, and then our groups develop follow-up assay to validate whether the compound really binds to the active site and confirm the activity of the target protein (activation or inhibition).
- We also have developed a novel recognition algorithm to rapidly screen and analyze thousands of potential ligands simultaneously, which can greatly accelerate your lead identification process.
- Our teams are capable of applying several methods to separate protein ligand complexes from unbound ligands such as ultrafiltration or molecular exclusion chromatography.
Reference
- Richard, B.; Van, B. Affinity Selection-Mass Spectrometry: Defining the Bioactive Compounds in Complex Mixtures of Natural Products and Combinatorial Libraries. The LCGC Blog. 2020, 18(1): 18-23.
※ It should be noted that our service is only used for research.

One-stop
Drug Discovery Services
- Experienced and qualified scientists functioning as project managers or study director
- Independent quality unit assuring regulatory compliance
- Methods validated per ICH GLP/GMP guidelines
- Rigorous sample tracking and handling procedures to prevent mistakes
- Controlled laboratory environment to prevent a whole new level of success
Online Inquiry

