MS for Structure Confirmation
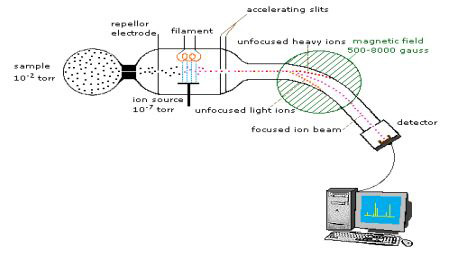
Fig.1 Diagram of Mass spectrum. (Sarvani, V.; et al. 2013)
Introduction to Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Analytical scientists widely rely on structure confirmation data of new compounds provided by mass spectrometry. MS is a useful approach for label-free high-throughput screening and has been applied to identify and characterize compounds, determine purities, and fragment-based screening in the drug discovery.
Principle of MS
Mass spectrometer has the ability to perform multiple steps of mass spectrometry on a single sample. It generates a mass spectrum and fragment the ion that is specifically selected from that spectrum, and generate another mass spectrum and repeat the entire cycle many times. In general, mass spectrometers produces ions from analyzed compounds that are separated on the basis of their mass-to charge ratio (m/z). MS therefore shows ability in deconstructing a complex molecule piece by piece until determine its structure.
Our Capabilities of MS Services
The facilities at BOC Sciences enable our researchers to investigate a broad range of mass spectrometric applications and we provide a diversity of mass spectrometry methods according your specific need:
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
We can utilize the comprehensive structural data obtained from LC-MS to identify the proteins and analyze the affinities.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS)
Our groups have developed a highly automated and extremely sensitive HPLC-MS method to support compound characterization and higher-throughput purification strategies.
Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry (CE-MS)
We use CE-MS to perform high resolution separation and conduct characterization with high sensitivity for the analysis of therapeutic biomolecules.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
GC-MS is a suitable approach to study the drug ligand candidates which interact with proteins non-covalently. Our scientists apply it in the identification of small molecule ligands by isolateing and analyzing the complexes.
Affinity Selection-Mass spectrometry (AS-MS)
We assess the binding events of candidate molecules and detect the protein–ligand complex directly with the application of AS-MS.
Our Advantages of MS Services
- Our experts have strong abilities in shortening operation cycle times, handling error recovery situations and providing more rapid result analysis to help accelerate the drug discovery process by automatizing mass spectrometry workflows.
- With an advanced platform in BOC Sciences, our team can integrate and perform full-length MS process with multiple units to accomplish your various sample processing tasks at the same time.
- We offer services of MS method conditions validation and the professional data analysis strategies to realize comprehensive characterization and assays of drug candidates.
Reference
- Sarvani, V.; et al. Role of LC-MS in drug dicovery process. International Journal of Pharmacy & Therapeutics. 2013, 4(3): 148-153.
※ It should be noted that our service is only used for research.

One-stop
Drug Discovery Services
- Experienced and qualified scientists functioning as project managers or study director
- Independent quality unit assuring regulatory compliance
- Methods validated per ICH GLP/GMP guidelines
- Rigorous sample tracking and handling procedures to prevent mistakes
- Controlled laboratory environment to prevent a whole new level of success
Online Inquiry

