BLI for Affinity-based Hit Screening
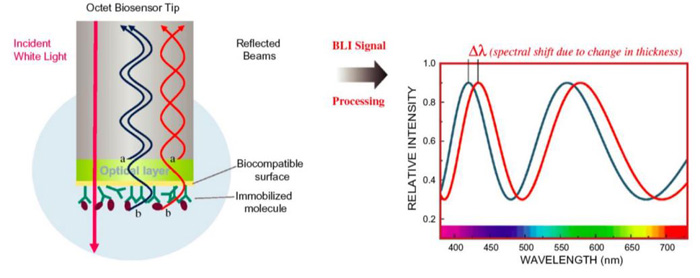
Fig.1 The assay principle of the BLI technology. (Nirschl, M 2011)
Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) Technology
BLI is an optical biosensor platform. In a BLI experiment, a target-layer is immobilized on the surface of a biosensor and a ligand-layer is surrounded by liquid which is flowing through the biosensor surface. BLI monitors interference patterns that are reflected from two optical layers combined with biosensor tip. The binding events can be determined by wavelength changes which are caused by the variety of optical thickness at the surface.Therefore, any change in the thickness of the outer target-layer reflects the change in wavelength shift and is be able to recorded in real time, proving it an useful assay technique to measure the binding affinity and kinetics of biological macromolecule interactions.
Advantages of BLI
- No fluids in BLI experiments which is easy for sample recovery.
- Label-free: No fluorescent dyes required and compatible with numerous coupling methods.
- Robust and free choice of assay buffers.
- Wide dynamic range: Detectable affinities from pM to mM.
- Wide range of molecules: From large VLPs to smaller molecules.
Services of Bio-Layer Interferometry
Binding kinetics
We offer rapid, accurate, and sensitive determination of kinetics by utilizing relevant parameters such as ka (association rate constant) which provides information on how fast complexes form, kd (dissociation rate constant) which provides information on how fast complexes dissociate and KD (equilibrium dissociation constant).
We help to select the most potential hits, study protein-protein/small molecule interaction and antibody characterization based on these useful data.
Affinity
We measure the steady-state affinity by the data of KD obtained by kinetic or classical equilibrium binding analysis and ΔH (binding enthalpy) of an binding interaction.
Our team conducts competition assay, such as confirming binding site by ligand competition, studying hit specificity in the presence of competitors and investigating mode-of-binding and mechanism of interaction.
Quantification
Our team can help quantifying target concentrations of biological macromolecules including proteins, antibodies, antibody fragments in supernatants, production mixtures, or crude lysates.
We are also capable of applying BLI in the application of antibody quantitation and protein quantitation.
Fragment-based screening
BOC Sciences has validated BLI for fragment screening and our teams have expertise and experience in providing biosensor-based fragment screening services.
We can offer high-quality screening with complex targets involved in protein-protein interactions and analyze the interactions between protein targets and fragments, reducing the false-positive rates largely in the process of hit finding.
Our Advantages of Bio-Layer Interferometry Services
- We are constantly improving the efficiency of bio-layer interferometry workflow to maintain it at a high-throughput level.
- Our team helps to develop a variety of antibody assay campaigns with their professional technology of affinity-based hit screening and epitope binning-based hit clustering.
- Our advanced BLI platform is designed and applied to offer ease-of-use and versatility capability in assay development.
- We can conduct screening of hundreds of candidates in a matter of hours with minimal material consumption, helping to shorten the timeline for novel drug discovery.
Reference
- Nirschl, M. Review of Transducer Principles for Label-Free Biomolecular Interaction Analysis. Biosensors. 2011, 1(3).
※ It should be noted that our service is only used for research.

One-stop
Drug Discovery Services
- Experienced and qualified scientists functioning as project managers or study director
- Independent quality unit assuring regulatory compliance
- Methods validated per ICH GLP/GMP guidelines
- Rigorous sample tracking and handling procedures to prevent mistakes
- Controlled laboratory environment to prevent a whole new level of success
Online Inquiry

