High Content Imaging (HCI)
High-content imaging is a form of microscopy technique that allows simultaneously screening multiple cells in high resolution. The aim of HCI is to detect subtle morphological and monitor phenotypic variation. HCI enables to image higher throughput and conduct faster screenings by involving the automated imaging and data analysis. High content imaging approach can be applied at the early stages of drug discovery and is able to to give critical guidance for follow-up experiments by using high-throughput image analysis of multiple compounds on cells.
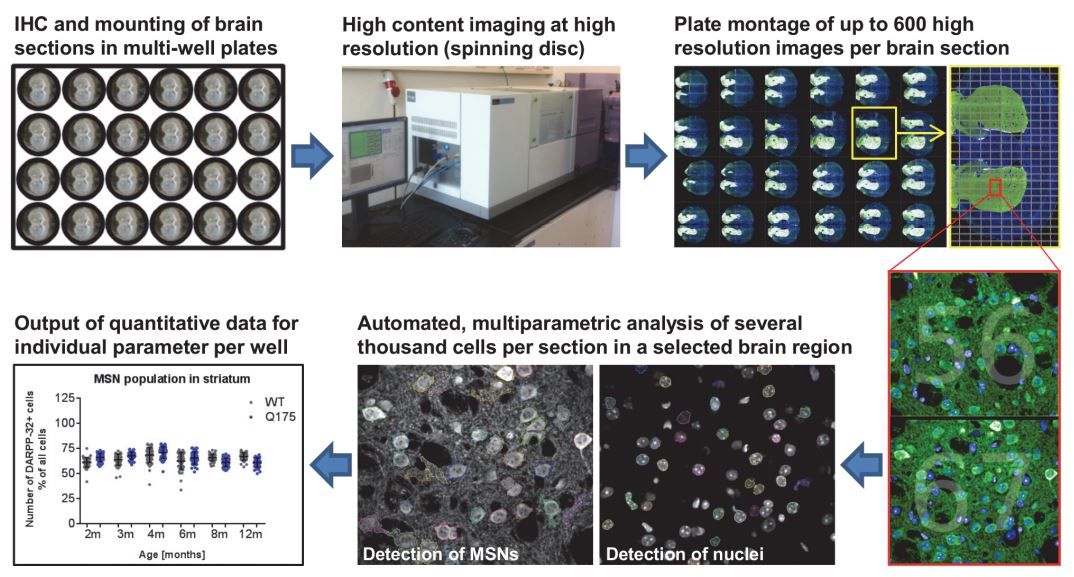 Fig.1 Workflow of high content imaging for ex vivo phenotypic characterization.
Fig.1 Workflow of high content imaging for ex vivo phenotypic characterization.(Nikisha, C.; et al. 2015)
Services
We are capable of offering hundreds of images of various chemical in multiple samples and capturing important data of high levels for the following steps of phenotypic assays and high content analysis.
Sample preparation
Multiple fluorescent markers available: Fluorescent dyes, fluorescently labelled proteins and fluorescently labelled antibodies.
Our HCI platform has developed HCI assays with the use of a diversity of immunofluorescence markers against endogenous proteins in 384- and 1,536-well formats.
Cell painting
We provide high-quality cell painting services to help our customers detect and quantify the binding events occurring between the compounds and ligands.
We can also analyze multiple profiles in the same sample well.
Imaging acquisition
The HCI infrastructure in BOC Sciences includes several confocal/widefield imaging systems and you can acquire hundreds of images at different XY positions at 4x to 60x magnifications with a relative high resolution.
Imaging analysis and quantification
We stitch these acquired hundreds of images together to get an overall image of an entire sample and perform quantitative analysis of large numbers of images and structures with different cells, shapes, sizes, and textures.
Data interpretation and visualization can be achieved by the combination of our quality control and statistical tools.
Live-cell kinetic imaging
Our HCI technique is also capable of developing, validating and performing live-cell kinetic imaging assays to optimize your hit identification process.
Our Advantages
We offer a customized automated analysis to identify the regions of your interest to support your hit identification.
Our HCI system is a fully-integrated solution that allows the analysis of more than 100 markers on a single sample and multiple samples at a time, which ensures a robust and fast high-throughput imaging experiments.
Equipment
BOC Sciences has designed and implemented a fully-integrated HCI platform which is equipped with advanced microscopy systems and sample carriers for ultra high content imaging:
MACSima Imaging Systems
Corning® Microplates for Microscopy and High Content Imaging
Reference
Nikisha, C.; et al. Characterization of HTT Inclusion Size, Location, and Timing in the zQ175 Mouse Model of Huntingtons Disease: An In Vivo High-Content Imaging Study. Plos One. 2015, 10(4).
※ It should be noted that our service is only used for research.

One-stop
Drug Discovery Services
- Experienced and qualified scientists functioning as project managers or study director
- Independent quality unit assuring regulatory compliance
- Methods validated per ICH GLP/GMP guidelines
- Rigorous sample tracking and handling procedures to prevent mistakes
- Controlled laboratory environment to prevent a whole new level of success
Online Inquiry

